In this brief blog, we will go over the high-level aspects regarding injection molding - what it is, the benefits, and how it generally works. Give us a shout if you think it might be a great fit for your next project or application!
What is injection molding?
Injection molding is a way to manufacture and produce parts in large quantities. It is often used in production scenarios where the exact same part is being produced over and over again in the thousands.
The main advantage of using injection molding is the ability to scale production in enormous portions, resulting in price per unit becoming much lower. While the initial investment may come with some added costs, it will eventually for itself over time and ultimately result in profit.
Benefits of Injection Molding
In addition to cost, there are major benefits when it comes to utilizing injection molding. Injection molding reduces the amount of scrap, which ultimately reduces waste. Unlike traditional manufacturing processes where the machine cuts away substantial amounts of the original block or sheet, injection molding has little to no scrap waste.
A second benefit, as we discussed earlier, is its repetition in the thousands over a short time period. When using injection molding, you can be sure that each piece will be nearly identical. This repetition works for both smaller and large quantities. It also helps with brand consistency as the process is highly reliable and can ensure that consumers can count on your brand.
Lastly, injection molding provides you with the ability to create exactly what you want. As an engineer or designer, you can design and prototype your specific part to your own specifications. Fine-tuning can continue with your product with little waste prior to mass producing it.
Anatomy of an Injection Mold
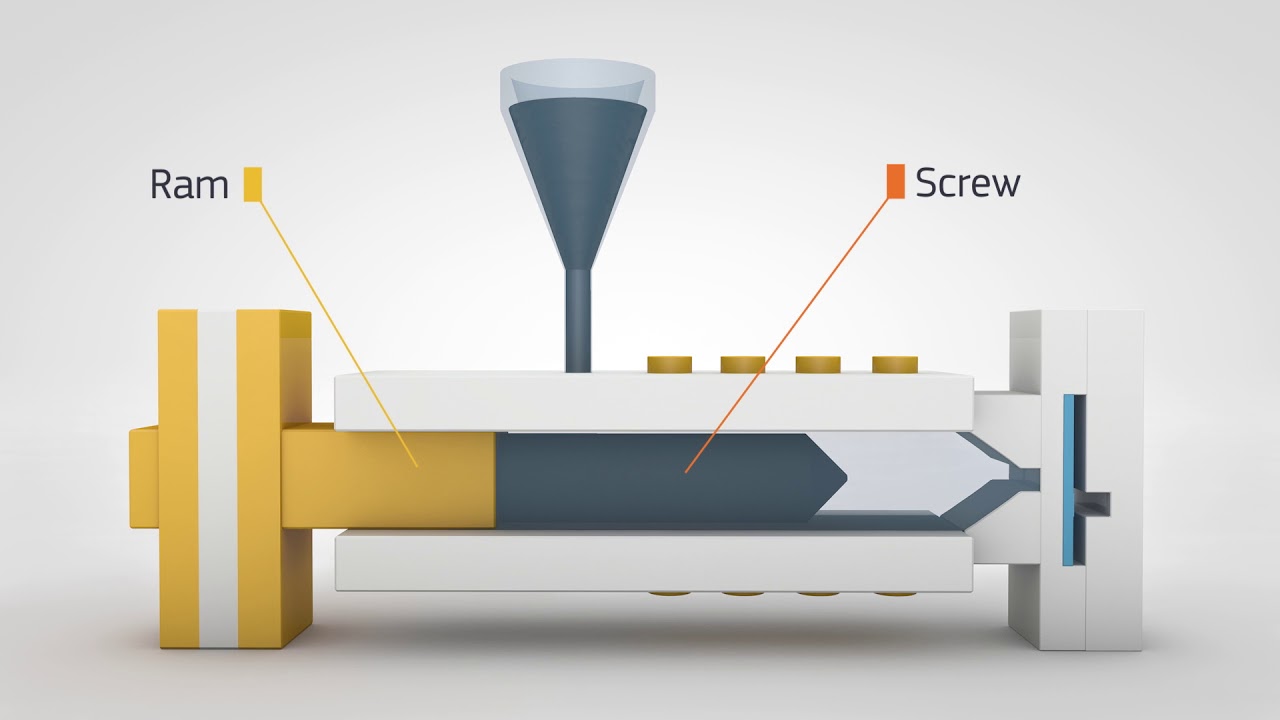
While injection molds look like complicated and detailed machinery, each of the device’s respective parts have a function that supports the mold creation.
Injection molding machines are also referred to as presses. They consist of a material hopper, an injection ram or screw-type plunger, and a heating unit.
Molds clamp to the platen of the molding machine. There, the plastic is injected into the mold through a part called the sprue orifice. Each injection mold needs to have an opening that allows the molten plastic to be injected into the cavity of the mold. Voila.
The original content for this article was written by Real Seal Co. and can be found on their website here.
Gallagher Fluid Seals partners with the world's best seal manufacturers. We can help bring your idea or project to life. For more information about injection molding, contact our engineering department today.
