Article re-posted with permission from Parker Hannifin Sealing & Shielding Team.
Original content can be found on Parker’s Blog.
What does a customer do when their application calls for enhanced performance that elastomers alone cannot offer? They turn to GFS partner, Parker Hannifin's uniquely formulated chemical bonding agents which enhance the performance of common elastomeric components by integrating them robustly with metal, thermoplastic, or other component substrates. Using world class process control during the elastomer’s vulcanization process, component substrates become integrally linked to the engineered elastomer, transforming them into a cohesive sealing system.

Features and benefits of advanced bonding technology for seals
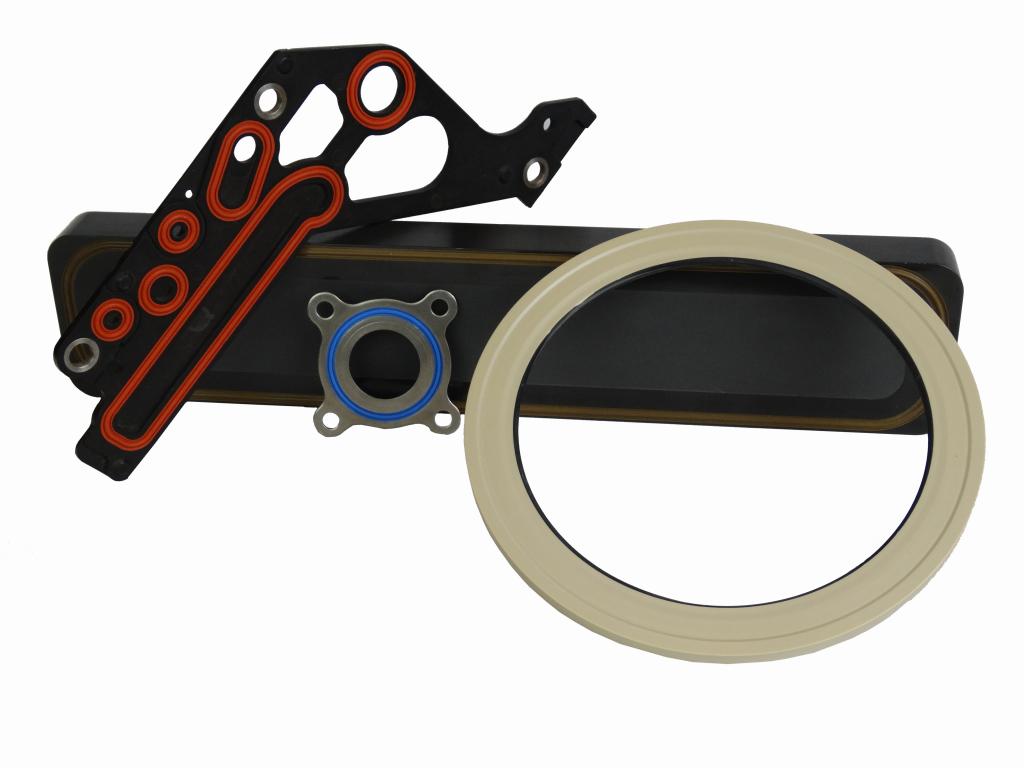
Bonded seals alleviate some of the most common issues with strictly elastomeric seals. They eliminate complicated installations, handling damage, and twisting or pinching problems common in other loose elastomeric seals, culminating in a reduction in the cost of installation and assembly for end users.
Bonded seals by design eliminate alternate leak paths, providing highest sealing performance as well as the most consistent sealability. One of the key features of bonded seals is that the retainer to which the elastomer is bonded acts as a secondary seal, thus transferring some sealing responsibility from the elastomer to the retainer.
Bonded seals also reduce machining costs by eliminating the need for machined seal grooves in the mating hardware. An added benefit of bonded seals is a controlled installation, limiting the amount of load placed on any seal due to the retainer.
So how exactly does it work?
There are three main components that go into creating a cohesively bonded sealing system:
- elastomeric formulations
- control of component substrate manufacturing
- bond chemistry development
Parker labs concurrently designs withParker engineering to ensure vulcanization complements the surface chemistries in the bonding process. Just as Parker chemists determine the chemical reactions taking place between bonding agents and component surfaces, Parker engineers must create an optimum processing environment devoid of surface contaminants to promote robust bonding reactions in true-to-life manufacturing environments.
What materials can you use?
Parker is constantly expanding its product offerings to meet the newest challenges presented by customers. Each combination of retainer substrate and elastomeric compound offers different characteristics. That being said, they have developed a variety of bonds that allow them to bond to:
- Aluminum
- Stainless Steel
- Brass
- PEEK
- Nylon
The compounds that can be bonded to these materials include but are not limited to:
- FKM’s
- FFKM’s
- FMVQ’s
- Hifluor materials
This chart shows a variety of retainers and compounds that Parker can bond using specific chemical bonds depending on the material and retainer combinations. With all of our bonds Parker uses standard test method ASTM D429 Methods B to validate the integrity and strength of our bonding systems.
For more information about bonding technology for seals, contact Gallagher Fluid Seals today.
